The Hilbert-transform
The Hilbert transform
Though it's use is frequent in signal processing, it does have a significance in understanding tomographic image reconstruction, the Hilbert transform.
. The 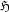 Hilbert transform is defined as:
Hilbert transform is defined as:
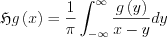
The definition looks simple, to evaluate the integral looks a lot harder as the denominator harbours a singularity. It means we have to take the integral in a Cauchy principal value, so
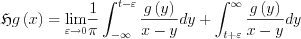
Existence of such a limit can easily imagined, as for function g=1 the function 1/x can be integrated in Principa Value, being odd the result is 0, since the range of the integral is symmetric.
To ease the evaluation of the integral
- note that the Hilbet transfrom is a convolution with function 1/x
- Fourier transform then inverse Fourier transform the expression
![$\mathfrak{H}g\left ( x \right )=g\left ( x \right )*\frac{1}{\pi x}=\mathfrak{F}^{^{-1}}\mathfrak{F}\left \{ g\left ( x \right )*\frac{1}{\pi x} \right \}=\mathfrak{F}^{^{-1}}\left \{ \mathfrak{F}\left [ g\left ( x \right ) \right ] \mathfrak{F}\left [ \frac{1}{\pi x} \right]\right \}](lib/equation/pictures/56692ccf511ffea2e62b02008c4b139a.png)
Let us evaluate the Fourier transform of 1/x:
![$\mathfrak{F}\left [ \frac{1}{x} \right ]=-\frac{1}{\pi}\int_{-\infty }^{\infty }\frac{e^{-i k x}}{x}dx=-\frac{1}{\pi}\int_{-\infty }^{\infty }\frac{\cos( kx)-i\sin\left ( kx \right )}{x}dx](lib/equation/pictures/5645e0dddef1aebfa55e5313e25ca71f.png)
The function cos is even, divided by the odd "x" function the first term is again zero.
We have the next two terms remaining:
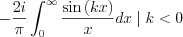
and
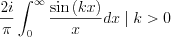
Since
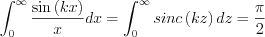
The result is, then:
![$\mathfrak{F}\left [ \frac{1}{x} \right ]=i sgn(k)](lib/equation/pictures/a83009ca44394f82218886976f8873e7.png)
where sgn is the sign function.
![$\mathfrak{H}g\left ( x \right )=\mathfrak{F}^{^{-1}}\left \{ \mathfrak{F}\left [ g\left ( x \right ) \right ] i sgn(k)\right \}](lib/equation/pictures/3c6498ec17ef4cf4f51f231fdacb65fe.png)
This result, regarding the numerical evaluation technique is a lot simpler then the application of the basic definition, since the digital Fourier transform and its implementation technique (FFT) is a routinely applied, accessible and fast.
Our results also shows, that if we apply the Hilbert transform twice on the same function we obtain:
![$\mathfrak{H}\mathfrak{H}g\left ( x \right )=\mathfrak{F}^{^{-1}}\left [\left \mathfrak{F}[\mathfrak{F}^{^{-1}}\left \{ \mathfrak{F}\left [ g\left ( x \right ) \right ] i sgn(k)\right \} \right ]i sgn(k) \right ]=-g\left ( x \right )](lib/equation/pictures/024a3676ff348ee229364409ce4e7d24.png)
thus the inverse of the Hilbert-transfrom is -apart from a sign- is itself.
As an illustration we have prepared the 2D Hilbert transform of an image:
|
|
|