The Radon Transform in multiple dimensions
The Radon transform in 2D means an integral taken along a parametrized 2D linear set (normally a straight line). In multiple dimensions a linear geometrical set can mean a line or a hyperplane, the latter leads us to the multi-D generalization of our previous definition of the Radon-transform, the former gives the Ray (or X-ray) transform.
Radon transform in multiple dimensions
Let us take the paramters 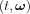 to describe a hyperplane (
to describe a hyperplane (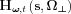 ), where according to the its y points the integrals are taken,
), where according to the its y points the integrals are taken, 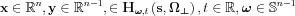 ), with that we have the definition of the Radon transform for an n dimensional function:
), with that we have the definition of the Radon transform for an n dimensional function:
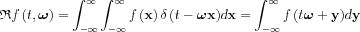
Ray-transform
If carry out the integral with regards to t, i.e. instead of a hyperplane we have a direction  and along that we do a line integration, we obtain the other possible generalization of the 2D Radon transform, called the (X-)Ray transform. With the definitions above the
and along that we do a line integration, we obtain the other possible generalization of the 2D Radon transform, called the (X-)Ray transform. With the definitions above the 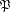 Ray transform is defined as:
Ray transform is defined as:
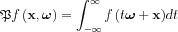
where it is enough to take the values of x from a plane perpendicular to vector  .
.
With these definitions we can construct the inverse of the Radon and the Ray transforms.
The original document is available at http://549552.cz968.group/tiki-index.php?page=The+Radon+Transform+in+multiple+dimensions